Evaluating flags
Read time: 19 minutes
Last edited: Feb 06, 2025
Overview
This topic explains how to use the flag evaluation feature to serve different feature flag variations to contexts and users. This feature is available for all of the LaunchDarkly SDKs.
About flag evaluation
The flag evaluation feature requires a feature flag key and the context that encounters the flag in your application. It returns the value of the feature flag variation for that context, based on the flag targeting rules you have created, including any prerequisite flags.
Every flag has at least two variations: one for when targeting is off, and one for when it's on. To learn more, read Creating flag variations.
This is an example of a flag with three variations:
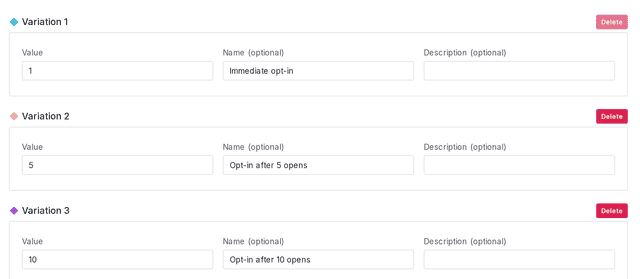
Flags also have fallback values. The fallback value is defined in your code, is one of the flag's variations, and is only returned if an error occurs. For example, the SDK serves the fallback value if LaunchDarkly is unreachable, the feature flag key doesn't exist, or the context or user doesn't have a key specified. It also serves the fallback value if it cannot authenticate, or if your LaunchDarkly account has been deleted.
If you are working with an older version of the SDK, you may provide a user object in the evaluation call. If you are using an SDK that supports contexts, and don't supply the context kind, then that object is automatically interpreted as a context with a kind of "user." To learn more, read Context kinds.
The flag evaluation feature adds a context to the Contexts list, if a context with the same key does not already exist. However, each SDK evaluates flags based only on the object you provide in the evaluation call. In other words, the SDK does not automatically use the attributes shown on the Contexts list, and attributes are not synchronized across SDK instances. You must provide all relevant attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly. To learn more, read Context configuration.
You do not need to create contexts or users manually, but if you want to, you can with the identify feature. To learn more, read Identifying and changing contexts.
The flag evaluation feature only returns information about the flag variation for the context. To access other information about a flag, visit the Flags list in the LaunchDarkly user interface. Alternatively, use the getFeatureFlag endpoint in LaunchDarkly's REST API.
Details about each SDK's configuration are available in the SDK-specific sections below:
Client-side SDKs
This feature is available for all of our client-side SDKs:
- .NET (client-side)
- Android
- C++ (client-side)
- Electron
- Flutter
- iOS
- JavaScript
- Node.js (client-side)
- React Native
- React Web: The React Web SDK relies on the JavaScript SDK for this functionality.
- Roku
.NET (client-side)
Expand .NET (client-side) code sample
The Variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to the current context. It requires the flag key and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In the client-side .NET SDK, there is a variation method for each type, such as BoolVariation or StringVariation.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
Android
Expand Android code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to the current context. It requires the flag key and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list. When LDClient is initialized for the first time at app launch, contexts receive the feature flag fallback values until an initial connection to LaunchDarkly completes.
In Android, there is a variation method for each type, such as boolVariation or stringVariation.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
C++ (client-side)
Expand C++ (client-side) code sample
The variation methods determine which variation of a flag is served to the current context. The variation method signatures take the feature flag key and a fallback value. When the client is initialized for the first time, contexts receive the feature flag fallback values until an initial connection to LaunchDarkly completes.
There are variation methods for each type, such as BoolVariation or StringVariation.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
To learn more, read the Client documentation.
Electron
Expand Electron code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific user. It requires the flag key and a fallback value. After the user is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
To evaluate any feature flag for the current user, call variation:
You must provide all relevant user attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
The return value of variation is always either one of the variations you defined for your flag in the flag's Variations tab, or the fallback value. The fallback value is the second parameter to variation.
You can also fetch all flags for the current user.
Here is an example:
This returns a key-value map of all your feature flags. It contains null values for any flags that could not be evaluated.
Both of these methods are synchronous. The client always has the last known flag values in memory, so retrieving them does not involve any input/output (I/O).
Flutter
Expand Flutter code sample
The variation methods determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to the current context. variation calls take the feature flag key and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list. When the client is initialized for the first time at app launch, end users receive the feature flag fallback values until an initial connection to LaunchDarkly completes.
In Flutter, there is a variation method for each type, such as boolVariation or stringVariation.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
To learn more, read boolVariation.
iOS
Expand iOS code sample
The variation functions determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves the current context. Variation functions take the feature flag key and a fallback value as parameters. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list. If the flag does not exist, cannot be cast to the correct return type, or the LDClient is not started, the function returns the fallback value.
In the iOS SDK, there is a variation method for each type, such as boolVariation or jsonVariation.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
JavaScript
Expand JavaScript code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to the current context. variation calls take the feature flag key and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example of the variation method:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
Node.js (client-side)
Expand Node.js (client-side) code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to the current context. It requires the flag key and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
React Native
Expand React Native code sample
The variation method determines the flag variation to serve for a specific context.
In React Native, there is a variation method for each type, such as boolVariation or stringVariation. In the React Native SDK version 10, there is also a hook for each type, such as useBoolVariation or useStringVariation.
Variation calls take the feature flag key and a fallback value. When ReactNativeLDClient is initialized for the first time at app launch, end users receive feature flag fallback values until an initial connection to LaunchDarkly is completed. You are not required to specify a context when you initialize ReactNativeLDClient. If you do not specify a context initially, end users will also receive fallback values until you do specify a context by calling identify(). To learn more, read Identifying and changing contexts.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
To learn more, read boolVariation.
The SDK also includes an untyped method to determine the variation of a feature flag. To learn more, read variation. We recommend using the strongly typed variation methods, such as boolVariation, which perform type checks and handle type errors.
React Web
The React Web SDK relies on the JavaScript SDK for this functionality.
The fallback variation for each flag is returned if an error occurs. For example, the SDK serves the fallback variation if LaunchDarkly is unreachable, the feature flag key doesn't exist, or the context or user doesn't have a key specified.
In the LaunchDarkly user interface, on the flag's Targeting tab, a value for the "Fallback variation" information appears. However, if you are using the React Web SDK this displayed value may not match the value actually being served for the fallback variation:
- A value for the fallback variation may appear in the UI even though you have not defined a fallback variation in your code. Specifically, the React Web SDK automatically uses the results of getting all flags to determine the value of the fallback variation. In some cases, this means that the fallback value is undefined. For example, it may be undefined if the SDK has not finished initializing, or if LaunchDarkly is unreachable.
- If you use the
useLDClient()hook and evaluate flags with the underlying JavaScript SDK'svariation()method, then you can define a fallback variation. However, the value displayed in the UI may not match the value of the fallback variation that you set in thevariation()call.
Rather than relying on the "Fallback variation" display in the UI, review your application code to determine the fallback variation that the SDK will serve if LaunchDarkly is unreachable.
Roku
Expand Roku code sample
The *variation methods determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to the current context. The calls require the flag key and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In the Roku SDK, there is a variation method for each type, such as boolVariation and intVariation.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
Server-side SDKs
This feature is available for all of our server-side SDKs:
- .NET (server-side)
- Apex
- C++ (server-side)
- Erlang
- Go
- Haskell
- Java
- Lua
- Node.js (server-side)
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- Rust
.NET (server-side)
Expand .NET (server-side) code sample
The Variation methods determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. The methods require the flag key, the Context to evaluate, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In .NET, there is a Variation method for each type:
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
Apex
Expand Apex code sample
The variation methods determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific user. In Apex, there is a variation method for each type, such as boolVariation or stringVariation. The methods take an LDUser, a feature flag key, and a fallback value. After the user is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant user attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
C++ (server-side)
Expand C++ (server-side) code sample
The variation family of functions determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. The functions require a context, feature flag key, and fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In C++, there is a variation function for each type, such as BoolVariation or StringVariation.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
Erlang
Expand Erlang code sample
The variation function determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. The functions take a flag key, context, fallback value, and an instance tag. In the example below, the fallback value is false. The instance tag is optional. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
Go
Expand Go code sample
The Variation methods determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. Variation methods take the feature flag key, a context, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In Go, there is a Variation method for each type:
BoolVariationIntVariationFloat64VariationStringVariationJSONVariation, which can be any JSON type.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly. To learn more about constructing the context, read Context configuration.
If you are using OpenTelemetry, then instead of using the Variation method for each type, you must use the VariationCtx method for each type. For example, use BoolVariationCtx rather than BoolVariation. The methods are the same except that the VariationCtx methods also require a Go context parameter. This Go context is used in the hook implementation that provides OpenTelemetry support. To learn more, read OpenTelemetry.
Haskell
Expand Haskell code sample
The variation family of functions determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. The functions take a Client, Context, feature flag key, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In Haskell, there is a variation function for each type:
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly. To learn more about constructing the context, read Context configuration.
Java
Expand Java code sample
The variation methods determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. The variation methods take the feature flag key, an LDContext, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In Java, there is a variation method for each type:
boolVariationintVariationdoubleVariationstringVariationjsonValueVariation, which can be of any JSON type.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
Lua
Expand Lua code sample
The variation family of functions determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. The functions take a context, feature flag key, and fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In Lua, there is a variation function for each type, such as boolVariation or stringVariation.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly. To learn more, read boolVariation.
Node.js (server-side)
Expand Node.js (server-side) code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. variation calls take the feature flag key, an LDContext, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
PHP
Expand PHP code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. variation calls take the feature flag key, an LDContext, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
Python
Expand Python code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. variation calls take the feature flag key, a Context, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly. To learn more about constructing the context, read Context configuration.
Ruby
Expand Ruby code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. variation calls take the feature flag key, an LDContext or user hash, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly. To learn more about constructing the context, read Context configuration.
Rust
Expand Rust code sample
The variation methods determine which variation of a flag LaunchDarkly serves to a specific context. variation methods take a Context, the feature flag key, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
In Rust, there is a variation method for each type:
bool_variation,int_variation,float_variation,str_variationfor strings, andjson_variation, which can be any JSON type.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant context attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly. To learn more about constructing the context, read Context configuration.
Edge SDKs
This feature is available for all of our edge SDKs:
Akamai
Expand Akamai code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a feature flag a context receives. variation calls take the feature flag key, an LDContext, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
To learn more, read variation. The LDClient also provides typed variation methods for type-safe usage in TypeScript: boolVariation, stringVariation, numberVariation, jsonVariation.
Cloudflare
Expand Cloudflare code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a feature flag a context receives. variation calls take the feature flag key, an LDContext, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
To learn more, read variation. The LDClient also provides typed variation methods for type-safe usage in TypeScript: boolVariation, stringVariation, numberVariation, jsonVariation.
Vercel
Expand Vercel code sample
The variation method determines which variation of a feature flag a context receives. variation calls take the feature flag key, an LDContext, and a fallback value. After the context is evaluated, you can view it on the Contexts list.
Here is an example:
You must provide all relevant attributes for each evaluation for your targeting rules to apply correctly.
To learn more, read variation. The LDClient also provides typed variation methods for type-safe usage in TypeScript: boolVariation, stringVariation, numberVariation, jsonVariation.